News
-

Separate maintenance of the suspension
Due to the increasing requirements of modern people for ride comfort and handling stability, non-independent suspension systems have gradually been eliminated. The independent suspension system is widely used by automobile manufacturers because of its good wheel touch ability, greatly impr...Read more -
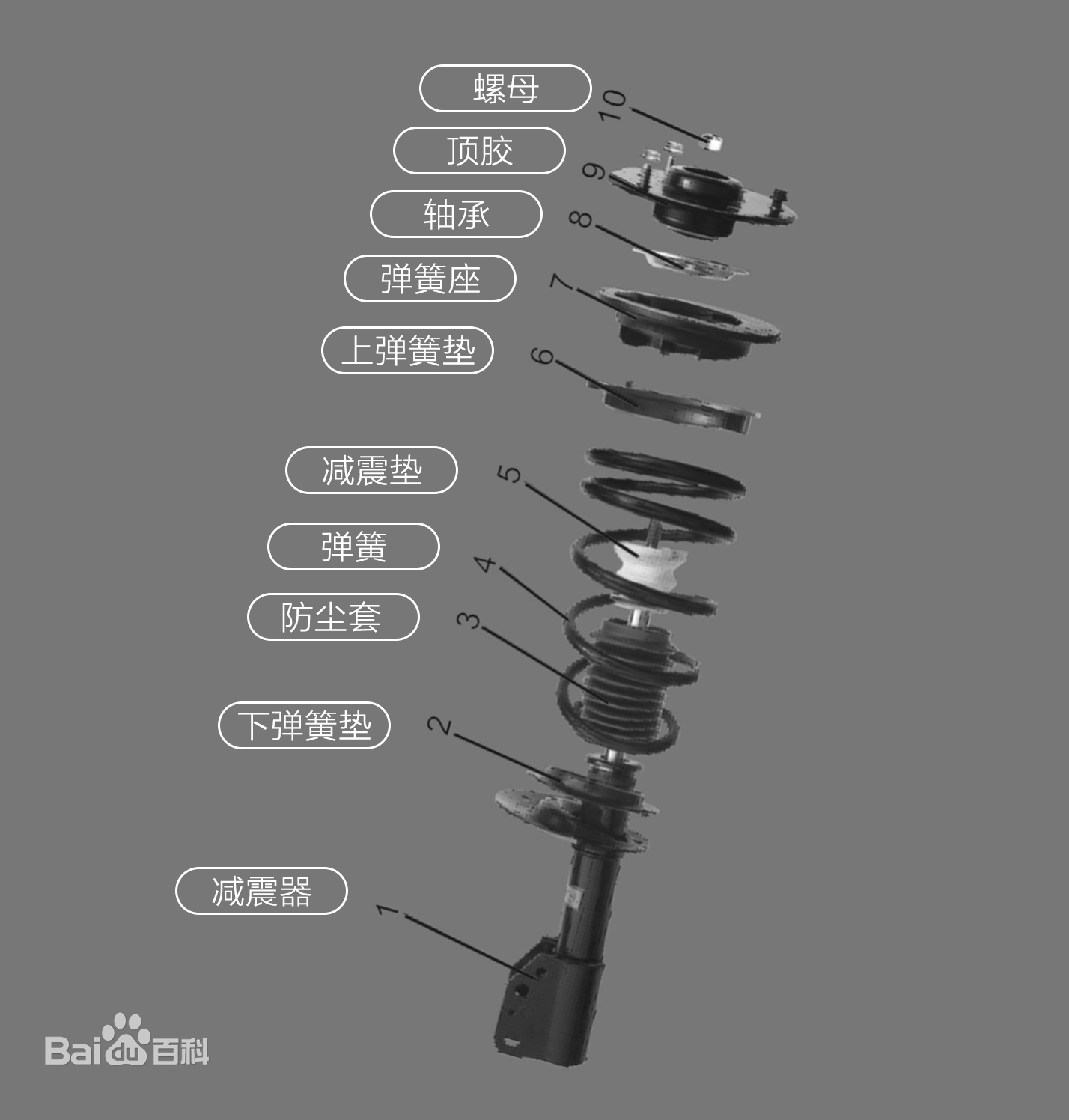
The replacement cycle of auto parts
1.tire Replacement cycle: 50,000-80,000km Replace your tires regularly. A set of tires, no matter how durable, won’t last a lifetime. Under normal conditions, a tire replacement cycle is 50,000 to 80,000 kilometers. If you have a crack on the side of the tire, even if you haven’t reac...Read more -
“Double 11″ e-commerce platform sales / automotive aftermarket in China
“Double 11″ e-commerce platform sales are hot, whether the automotive aftermarket can be boosted Double 11 is a popular event for live e-commerce, and it is also the largest bonus traffic for e-commerce. This year’s Double 11, more and more physical shopping malls and stores par...Read more -
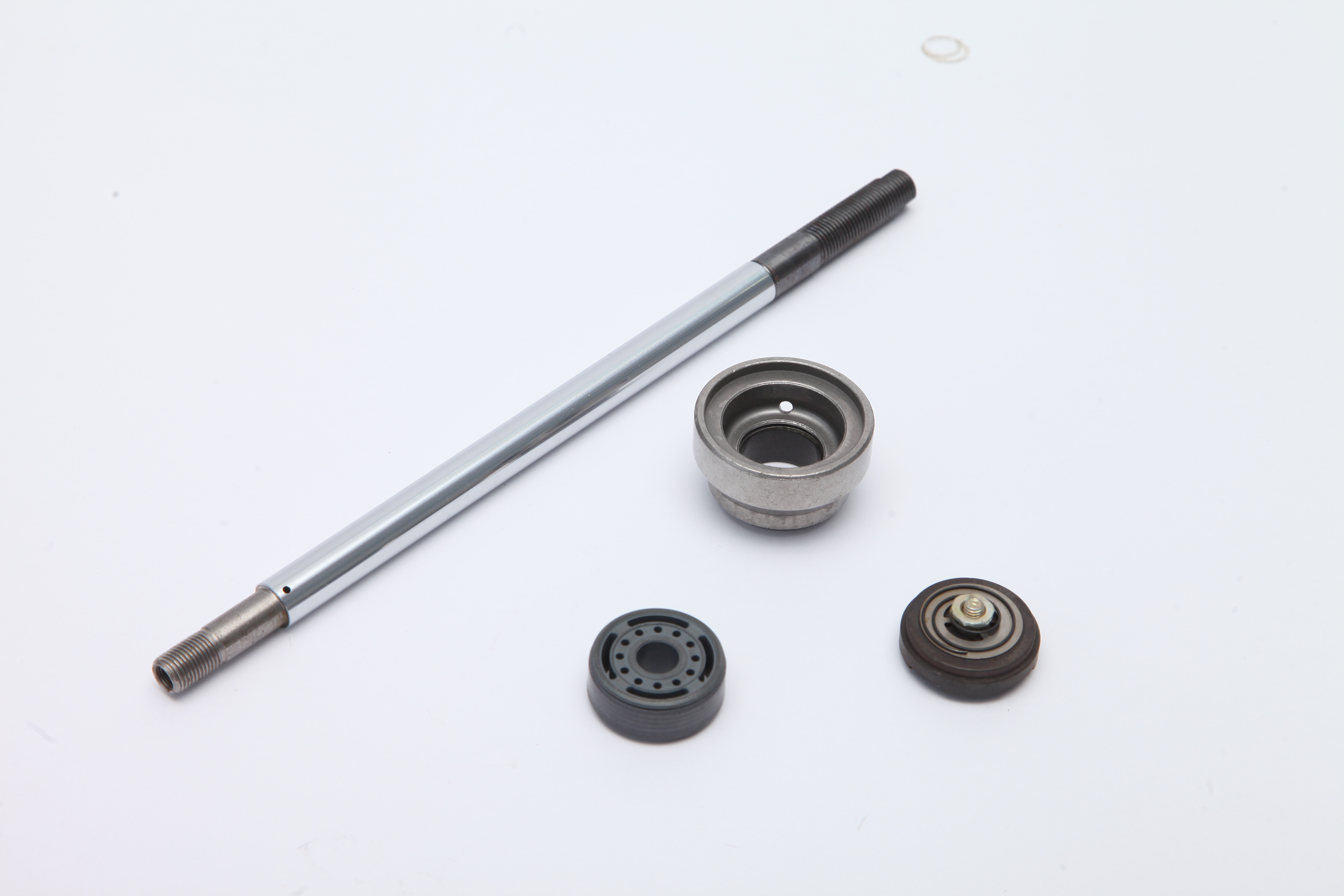

Piston rod details
The piston rod is a connecting part that supports the work of the piston. It is a moving part with frequent movement and high technical requirements, which is mostly used in the moving parts of the oil cylinder and the cylinder. Taking the hydraulic cylinder as an example, it is composed of cyli...Read more -

Visit us at MEXICO-CHINA INVEST&TRADE EXPO 2022
We are attending MEXICO-CHINA INVEST&TRADE EXPO 2022 Date: 8-10th NOV. 2022 Welcome to visit us, our booth no. 104Read more -
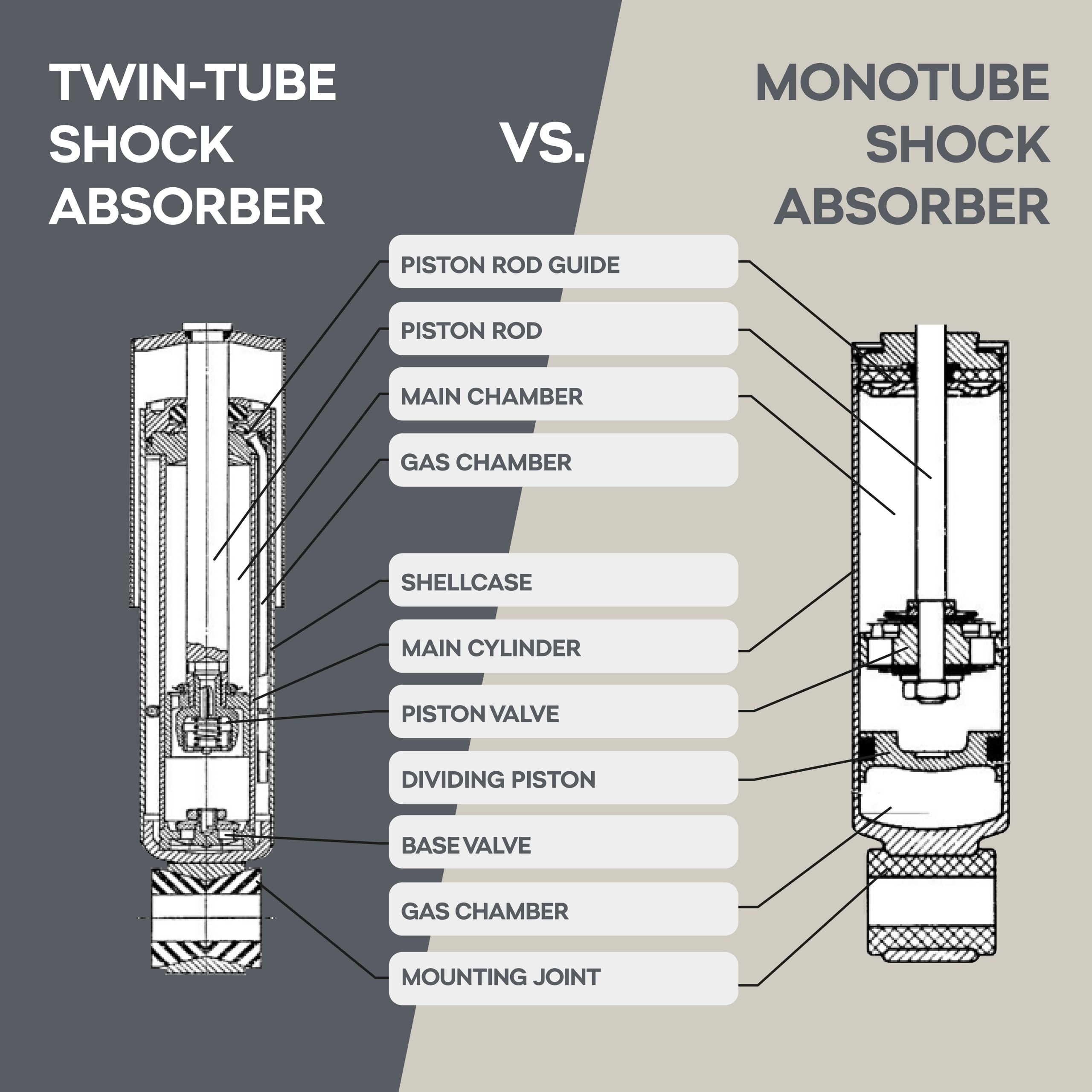
Car Shock Absorber Basics Knowledge
Shock absorbers are an essential part of the entire suspension system of a car, they improve comfort and prevent mechanical problems. Shock absorbers are hydraulic devices that both control and dampen shocks caused by the movement of the car’s springs and suspension. Therefore, its function...Read more -

Auto Aftermarket “Red Sea”? Industry changes lead to new trends
As a trillion-dollar market, the automotive aftermarket used to be a huge blue ocean in the eyes of investors and entrepreneurs, but in recent years, with the evolution of the market and the influence of various “black swan” factors, the automotive aftermarket has become more and ...Read more -
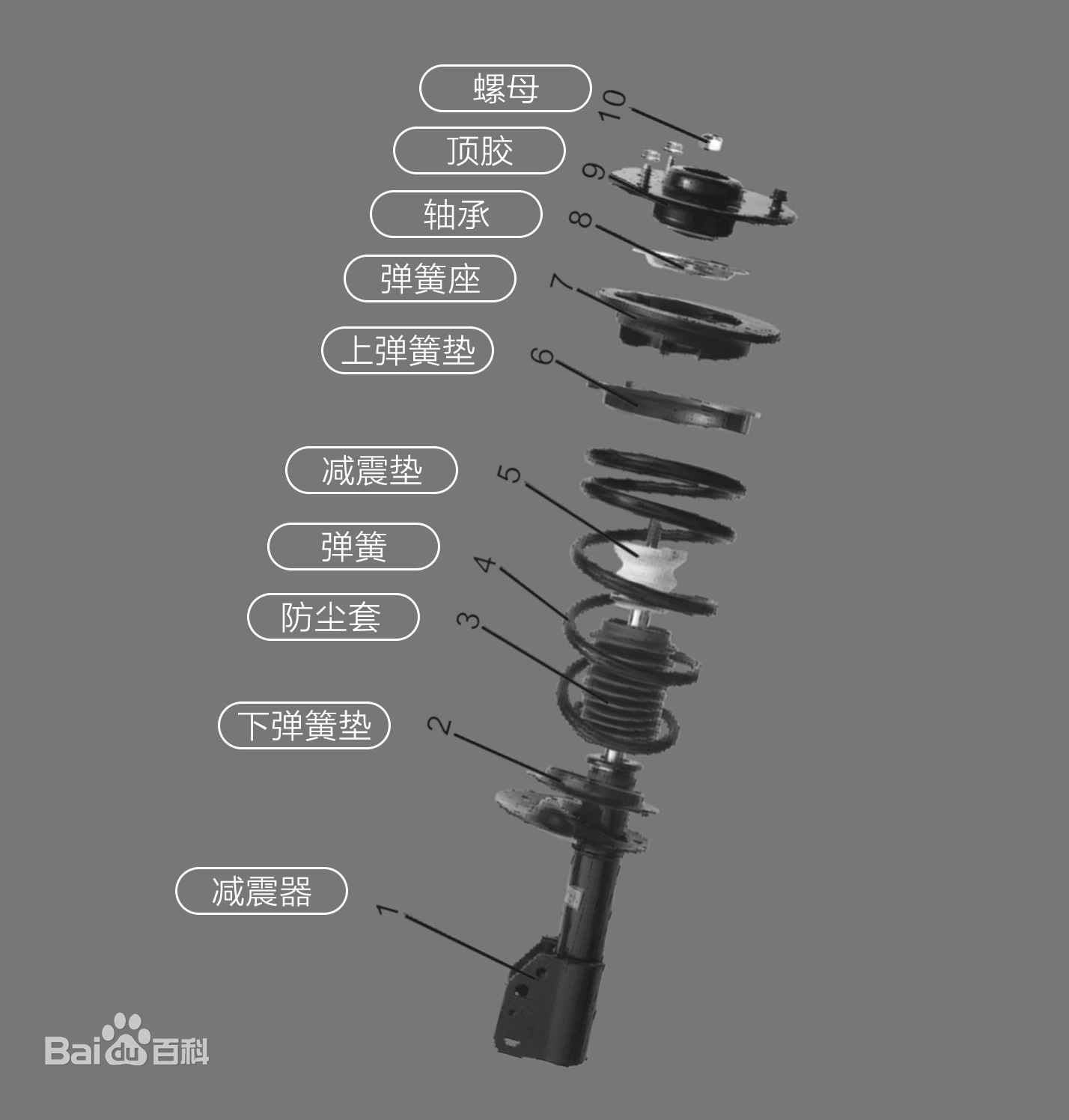
Basic Knowledge of vehicle suspension system -1
一.The suspension type ✔ The front suspension is the connection between frame and axle, in order to support the weight of the car, to absorb the vibration of the tyre, at the same time set up part of the steering device, according to the form of a front axle can be divided as follows. 1...Read more -
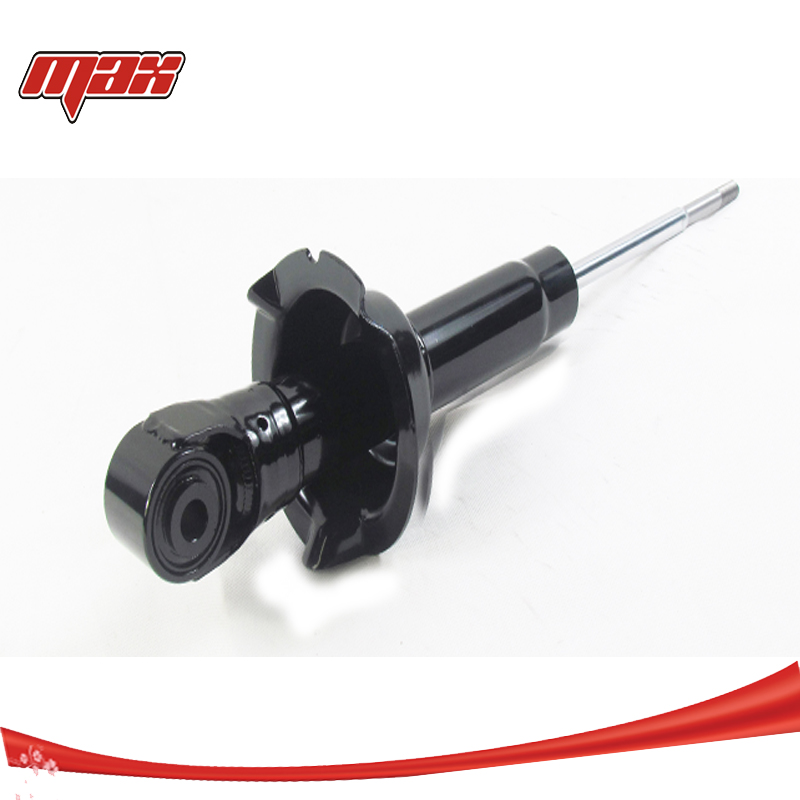

Automobiles Shock absorbers checking bugs
In order to make the frame and body of the vibration of the rapid attenuation, improve the ride and comfort of the car, the car suspension system is generally equipped with shock absorbers, the automobile is widely used in the bidirectional role of the cylinder shock absorber. Brief introduction...Read more -

How to solve the abnormal sound of top strut mount
How to solve the abnormal sound of top strut mount 1.The shock absorber needs to be removed for butter daubing. The abnormal sound of shock absorber top mount needs to be replaced with a new shock absorber top mount. 2. When the shock absorber is damaged due to serious wear and tear, the vehicle ...Read more -
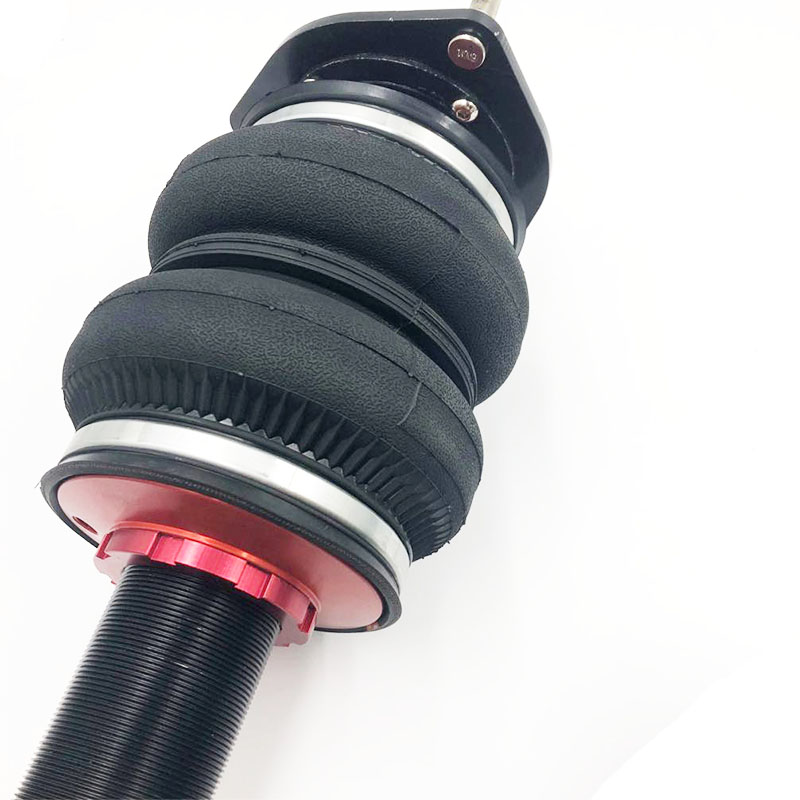

How to Judge Truck air bags work well or not ?
Airbag in order to make the vibration of the frame and the body cab rapidly attenuates, improve the ride comfort and comfort of the car, the car suspension system is generally equipped with shock absorber or air bag damping, the automobile is widely used in the two-way cylinder shock absorber.. ...Read more -

How long is the life span of the shock absorber
Air shock absorbers have a life span of about 80,000 to 100,000 kilometers. Here’s how it works: 1.the car air shock absorber is called the buffer, it through a process called damping to control the undesired spring movement. The shock absorber can slow down and weaken the vibration motion ...Read more











